Para consultas sobre nuestros productos o lista de precios, déjenoslo y nos pondremos en contacto dentro de las 24 horas.
Sociedad Americana de Pruebas y Materiales
(ASTM)
Métodos de prueba ASTM F2412-18 y
Especificaciones ASTM F2413-18
La norma ANSI Z41 fue retirada en marzo de 2005 y reemplazada por las normas ASTM.
Las normas ASTM F2412-05 y ASTM F2413-05 se publicaron para proporcionar métodos de prueba y normas de rendimiento, respectivamente, para el calzado de protección individual (PEI) que se comercializará en Estados Unidos. Se volvieron a publicar en 2011 y en 2017 y 2018.
Los cambios más recientes se resumen a continuación.
1. Muchos cambios editoriales para aclarar los requisitos, la agrupación de productos y la necesidad de recalificar todos Producto dentro de un año a partir de la publicación de la nueva fecha estándar del año
2. Introducción de diferentes niveles de protección SD
3. Eliminación de '/75' de las marcas I/75, C/75 y Mt/75
4. Requisitos recientemente agregados para el contenido de los informes de laboratorio de terceros
5. Se agregó un nuevo requisito para que un laboratorio externo emita un Certificado de conformidad.
Todo calzado certificado según ASTM F 2413 debe proporcionar resistencia al impacto y a la compresión como se especifica en las secciones 5.1 y 5.2 de la norma – marcas I y C.
Se puede proporcionar protección adicional dentro del calzado y los requisitos para ésta se detallan en las secciones 5.3 a 5.7 de la norma.
Sección 5.3 Protección metatarsiana (Mt)
Sección 5.4 Calzado conductor (Cd)
Sección 5.5 Calzado resistente a descargas eléctricas (EH)
Sección 5.6 Calzado disipativo estático (SD)
Sección 5.7 Resistencia a la perforación de la suela (PR)
CATEGORÍAS DE PRODUCTOS (AGRUPACIÓN) Y PRUEBAS DE CALIFICACIÓN
El calzado protector se clasifica primero en categorías de productos (grupos) donde cada miembro del grupo tiene la misma suela/entresuela (diseño, compuesto y dureza), horma, puntera, protección metatarsiana, método de construcción y los materiales de la parte superior, el forro, la plantilla y la inserción del cojín deben tener el mismo grosor +/- 12,5 %.
La categoría puede contener muchos patrones que varían en el diseño superior y se pueden agregar nuevos patrones a una categoría particular en cualquier momento.
Se requieren pruebas de calificación para todas las categorías nuevas, 3 pares de calzado (talla 9 y 10 para hombres)
Las tallas 8 para mujer deben probarse en un laboratorio independiente y obtener resultados satisfactorios antes de que se puedan marcar como conformes con la norma ASTM F2413. NOTA: Se necesitan 3 pares adicionales de la misma talla que la anterior. Prueba de impacto metatarsiano.
Las pruebas de recalificación son necesarias cuando se realiza algún cambio en el calzado existente que pueda afectar los resultados del área de prueba. Esta área se define como la parte delantera de un plano ubicado 25,4 mm (1 pulgada) detrás del borde posterior de la puntera protectora.
Cambios como los que se muestran a continuación requieren una nueva calificación:
1) Cambios en los materiales de la puntera protectora, la plantilla protectora o la protección metatarsiana.
2) Cambios en el diseño o proveedor de la puntera protectora, plantilla protectora o protección metatarsiana.
3) Cambios en el compuesto de la suela, incluido cambio de dureza.
4) Cambios en el método de construcción
5) Un cambio de fábrica de fabricación del calzado.
6) Cambios en el espesor (mayor al 25%) de los materiales utilizados para la parte superior, el forro, la suela o
porciones de la plantilla del calzado
7) Cambios en la forma de la horma.
Si el cambio no se aplica a todo el calzado de una categoría existente, se establece una nueva categoría para los diseños modificados. Si el cambio se aplica a todo el calzado, se recalifica toda la categoría de producto.
REQUISITOS
Resistencia al impacto (5.1) y a la compresión (5.2) – Marcas I y C respectivamente
Hay un nivel de protección disponible para resistencia al impacto (I) y a la compresión (C).
La puntera debe ser parte integral del diseño del calzado; la norma no cubre el uso de ‘Dispositivos de protección para los dedos del pie complementarios del mercado de accesorios.
Impacto | Compresión |
I = 75 ft. lbf (101,7 julios) | C = 2500 libras (11,121 newtons) |
Las distancias de prueba después de las pruebas de impacto y compresión son:
Para hombres: 0,500 pulgadas (12,7 mm)
Para mujeres: 0,468 pulgadas (11,9 mm)
Nota: Cada puntera protectora deberá llevar el nombre, la marca registrada o el logotipo del fabricante. El número o la identificación de la puntera, así como la talla de la puntera y la R (derecha) o L (izquierda), deberán estar estampados o marcados de forma permanente en un lugar visible.
Nota: Se especifica una prueba para comprobar que la plastilina sea de la calidad correcta y no demasiado dura ni demasiado blanda. Esta prueba debe realizarse al menos una vez cada seis meses.
Metatarsiano (5.3) – Marcado Mt
La protección metatarsiana está diseñada para prevenir o reducir lesiones cuando las áreas de los dedos y los metatarsianos del pie están expuestas a peligros de "caída".
El calzado que ofrece protección metatarsiana debe diseñarse y fabricarse con protectores metatarsianos integrados. La norma no contempla el uso de protectores adicionales.
La energía del impacto es la misma que la del impacto con el pie.
Las distancias de prueba después de las pruebas de impacto metatarsiano son:
Para hombres: 1 pulgada (25,4 mm)
Para mujer: 0,937 pulgadas (24 mm)
Calzado conductor (5.4) – Marcado CD
El calzado conductor está diseñado para descargar la electricidad estática del cuerpo del usuario a través del calzado. El suelo debe estar limpio y contar con una buena conexión a tierra para que la electricidad estática se descargue rápidamente. El calzado conductor está diseñado y fabricado para, en la medida de lo posible, eliminar el riesgo de que las chispas de electricidad estática incendien sustancias químicas volátiles o explosivos.
Nota: El personal que trabaja cerca de fuentes de electricidad expuestas no debe usar calzado conductor.
circuitos.
Todas las partes metálicas externas expuestas deben ser no ferrosas. No se permiten clavos de fijación de elevación superior expuestos.
permitido.
La resistencia eléctrica del calzado de protección conductor probado a 500 V deberá estar comprendida entre 0 y 500.000 ohmios.
Protección contra descargas eléctricas (5.5) – Marcado EH
El calzado de protección EH está diseñado para reducir los riesgos debidos al contacto accidental con corrientes de aire.
circuitos eléctricos (600 Voltios) y conductores o partes energizadas eléctricamente.
La superficie exterior de la suela y del talón no debe ser penetrada por ningún material conductor de electricidad.
componente.
El calzado resistente a descargas eléctricas debe ser capaz de soportar la aplicación de 18.000 voltios a 60 Hz durante 1 minuto sin flujo de corriente ni fugas superiores a 1,0 miliamperios en condiciones secas.
Calzado disipador de estática (5.6) – Marcado SD 10, SD 35 y SD 100
El calzado de protección SD está diseñado para reducir la acumulación excesiva de electricidad estática
conduciendo la carga corporal hasta el suelo manteniendo un nivel de resistencia suficientemente alto que protege al usuario de peligros eléctricos si entra en contacto con circuitos eléctricos activos.
No se permiten uñas expuestas en el calzado SD.
El calzado debe acondicionarse durante un mínimo de 24 horas a 21,1 ± 1,1 °C (70 ± 2 °F) y 50 ± 2 % de humedad relativa antes de la prueba y luego debe ser usado por el sujeto de prueba durante 5 minutos antes de probar la resistencia del pie izquierdo, el pie derecho y el par.
Las normas de 2005 y 2011 cubrían solo una clasificación SD y ésta es ahora la clasificación SD 100.
Para el calzado con clasificación SD 100, la resistencia eléctrica a 50 V probada a través del usuario debe ser mayor a 106 ohmios (1 megaohmio) y no exceder los 108 ohmios (100 megaohmios).
Para el calzado con clasificación SD 35, la resistencia eléctrica a 50 V probada a través del usuario debe ser mayor a 106 ohmios (1 megaohmio) y no exceder los 35 x 106 ohmios (35 megaohmios).
Para el calzado con clasificación SD 10, la resistencia eléctrica a 50 V probada a través del usuario debe ser mayor a 106 ohmios (1 megaohmio) y no exceder los 107 ohmios (10 megaohmios).
Calzado resistente a la perforación de suela (5.7) – Marcado PR
El calzado resistente a perforaciones incluye un dispositivo resistente a las perforaciones en la suela (generalmente debajo de la plantilla) que reduce la posibilidad de heridas por punción en la planta del pie si el usuario pisa objetos afilados que penetran las suelas del calzado.
El dispositivo de protección debe cubrir la máxima superficie posible del antepié y del talón.
La construcción lo permitirá. Además, las placas deben estar estampadas para identificar el nombre del fabricante (o nombre comercial) y el mes y año de fabricación.
Se deben probar tres pares (de tamaños aleatorios) de dispositivos resistentes a la perforación como artículos separados, y deben soportar una fuerza mínima de penetración de clavos de 270 libras (1200 Newtons). Además, las placas metálicas no deben mostrar signos de corrosión tras ser expuestas a una solución salina al 5 % durante un mínimo de 24 horas, de acuerdo con la norma ASTM B117, ni tampoco deben presentar signos de agrietamiento tras ser sometidas a 1,5 millones de flexiones, según la norma CAN/CSA Z195.
Al probar dispositivos resistentes a la penetración que no sean de metal, la punta del clavo no debe atravesar el dispositivo y debe ser visible en el lado del pie del mismo cuando se aplica la fuerza total de 1200 N.
ETIQUETADO E IDENTIFICACIÓN (6.1)
Al menos un medio par deberá estar etiquetado de forma clara y legible con letras y números no inferiores a 0,125
pulgadas (3,175 mm) de alto. La identificación deberá estar cosida, estampada o de otra manera duradera.
etiquetada. La identificación debe estar encerrada en un borde rectangular y colocada en el interior o
superficie exterior de la lengüeta, del refuerzo, del eje o del revestimiento del cuarto.
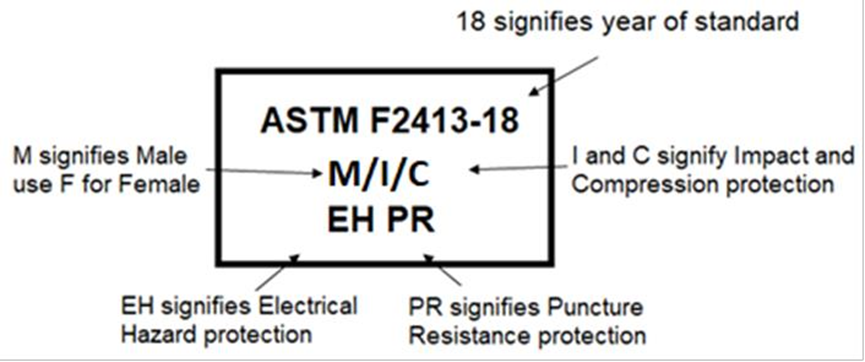
Se especifica un formato específico de 3 líneas para la etiqueta
Línea uno – ASTM F2413-18
Línea dos: F (hembra) o M (macho) e I (protección contra impactos) y C (protección contra compresión)
Línea tres: se utiliza para hacer referencia a las propiedades de protección adicionales proporcionadas y deben aparecer en el orden en que aparecen en la norma y en este manual. Mt, Cd, EH, SD 100 (35 o 10), PR
Las letras y números deben tener una altura mínima de 3,175 mm.